What is Salesforce Flow?
Salesforce Flow is a popular automation tool in the Salesforce ecosystem. It allows users to effortlessly streamline complex business processes. Offering both low-code and no-code options eliminates the need for extensive coding. Flow is designed with an intuitive visual interface for workflow design which ensures accessibility for users, regardless of technical expertise.
Our very own Salesforce Developers, Admins & Consultants at Prodigy use flow on a daily basis. Let’s explore some of the reasons for this here:
Enhanced Versatility
At the core of Salesforce Flow lies its ability to automate and optimize various business operations, including data entry, record updates, and approval workflows. This versatility shines through in the creation of interactive, dynamic, and efficient solutions. The inclusion of conditional logic empowers users to implement actions such as assignments, decisions based on various criteria, and loops for iterative processes, fostering flexibility and responsiveness in their workflows.
Broadened Capabilities
Salesforce Flow not only facilitates seamless interactions with screen elements but also supports the execution of actions such as lead conversion and the ability to auto-launch additional flows within a larger workflow. Its integration capabilities extend to various Salesforce functionalities, including Apex code, external systems and third-party tools found on the AppExchange.
There is no need to start building flows from scratch either, Salesforce has a tonne of pre-built flow templates tailored for common use cases. A user can customize these templates easily enough and align them with their specific requirements, significantly reducing the time and effort needed to set up flows. Furthermore, flows can be optimized for mobile devices, ensuring users can interact with them on multiple platforms.
Building Blocks
Every Salesforce Flow comprises three fundamental building blocks that combine to create seamless automation:
- Elements

These act as the foundational units of a Flow,. Elements execute logical actions such as assignments, decisions, or loops. Additionally, there are data elements capable of querying the database or effecting record changes. - Connectors
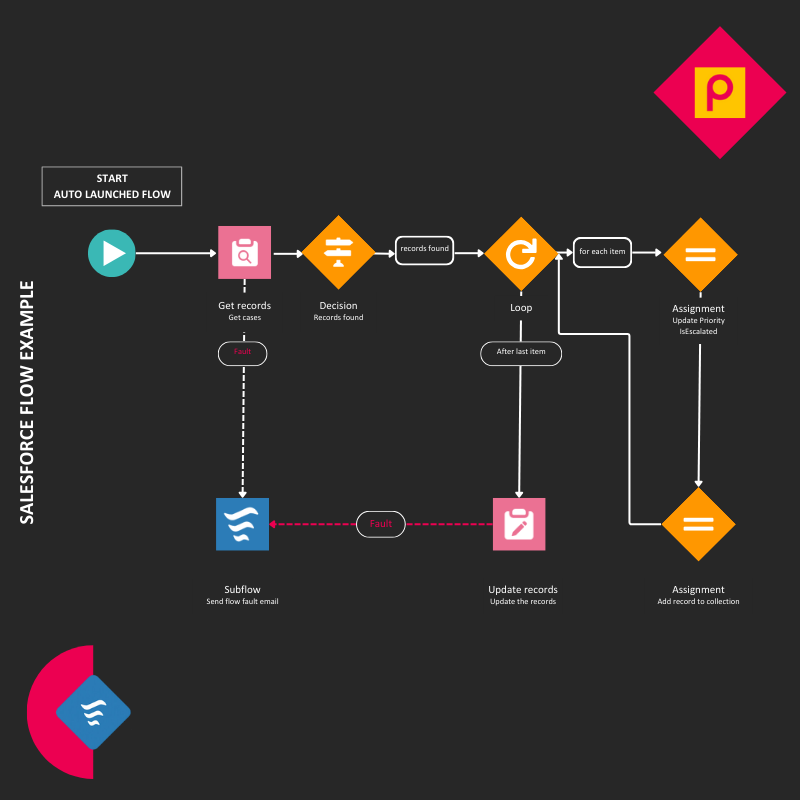
Connectors determine the flow of Elements, specifying how one element leads to another. Salesforce Winter Release ’21 introduced Auto-Layout, enabling automatic connection of Elements for a more intuitive design process for users - Resources
And then we have Resources. These are the individual data variables utilized within a Flow. These variables encompass text strings, numbers, records, formulas, or collections, contributing to the dynamic nature of the automation process.
Flow Types
Salesforce offers a spectrum of Flow types, each catering to specific business needs and scenarios:
- Screen Flow
Purpose: Guides users through business processes or collects real-time input.
Example: Registration pages, quick details pages, or contact forms, where users follow a guided process. - Record Triggered Flow
Role: A replacement for workflow rules and process builders.
Execution: Activated when a record is created, updated, or deleted.
Note: Limited to three execution points – Before Create/Update, After Create/Update, and Before Delete. - Autolaunched Flow
Nature: Operates as a sub-flow with no user interface (headless flow).
Activation: Triggered automatically based on specific circumstances, such as DML operations (Insert, Delete, Update).
Invocation: Can be called through Apex classes and other Flows
Function: Can be scheduled to run once, frequently, or regularly based on specified criteria.
Execution: Executes flow interviews for each record in a batch, with field values stored in the global variable $Record. - Platform Event-Triggered Flow
Capability: Enables comprehensive automation triggered by platform events.
Flow Activation: Initiated by users upon receiving a platform event message, providing access to every record.
Advantages: Streamlines automation processes, consolidating actions that previously required Process Builder and Flow Builder. Check out this article for Salesforce Admins: https://admin.salesforce.com/blog/2023/what-is-a-platform-event-triggered-flow
Flows & their use cases across business units
- Lead Management:
Lead Qualification Workflow:
Use Case: Implement a Flow to guide sales teams through a structured qualification process, ensuring consistent and thorough lead evaluations before progressing further in the sales pipeline.Lead Status Updates:
Use Case: Employ Salesforce Flow to automatically update lead statuses based on user interactions or specific triggers, streamlining the lead nurturing process and improving sales visibility.Lead Conversion Optimization:
Use Case: Create a Flow to automate lead conversion processes, ensuring that all necessary information is captured, associated records are updated, and relevant tasks are generated for a seamless transition to an opportunity.Lead Nurture Campaigns:
Use Case: Utilize Flows to trigger automated email campaigns or other marketing activities based on lead behavior, ensuring timely and personalized follow-ups to nurture leads through the sales funnel. - Rev Ops (Revenue Operations):
Use Case: Implement Salesforce Flow to automate the entire Quote-to-Cash process, ensuring smooth collaboration between sales, finance, and operations for efficient revenue generation.
Deal Desk Approvals:
Use Case: Streamline deal approval processes by creating a Flow that automatically routes deal-related requests to the appropriate stakeholders, ensuring quick decision-making and minimizing bottlenecks.Revenue Recognition Workflows:
Use Case: Design Flows to automate revenue recognition tasks, ensuring compliance with accounting standards and providing real-time visibility into revenue streams for the finance team.Renewal Management:
Use Case: Use Salesforce Flow to automate renewal workflows, providing timely alerts, generating renewal opportunities, and facilitating the renewal process for subscription-based businesses.Cross-Sell and Upsell Automation:
Use Case: Employ Flows to identify cross-sell and upsell opportunities within existing accounts, automatically triggering relevant actions and notifications to the sales team for maximizing revenue potential. - Customer Support:
Use Case: Implement Salesforce Flow to automate the assignment of support cases to the appropriate support agents based on workload, expertise, or other relevant criteria.
Automated Case Escalation:
Use Case: Create Flows to automatically escalate support cases based on defined criteria such as resolution time, customer priority, or severity, ensuring prompt attention to critical issues.Customer Feedback Surveys:
Use Case: Utilize Salesforce Flow to automate the distribution of customer feedback surveys after case resolution, collecting valuable insights to improve support services.Service Level Agreement (SLA) Management:
Use Case: Implement Flows to monitor and enforce SLAs, automatically notifying support teams and managers when cases are at risk of breaching defined service levels.Knowledge Base Updates:
Use Case: Use Flows to automate the updating of the knowledge base with resolved cases, ensuring that support teams have access to the latest information for efficient issue resolution. - Field Service
Work Order Assignment:
Use Case: Employ Salesforce Flow to automate the assignment of work orders to field service technicians based on location, skillset, or workload, optimizing field service operations.Inventory Management Workflows:
Use Case: Design Flows to automate inventory management tasks, such as stock level monitoring, reordering processes, and updating stock records based on field service activities.Route Optimization:
Use Case: Implement Flows to automatically optimize field service routes based on factors like location, traffic, and priority, ensuring efficient resource utilization and timely service delivery.Appointment Scheduling:
Use Case: Utilize Salesforce Flow to automate appointment scheduling processes, taking into account technician availability, customer preferences, and service level agreements.
Mobile Work Order Execution:
Use Case: Create Flows to enable field service technicians to execute work orders seamlessly on mobile devices, providing real-time updates, capturing customer signatures, and ensuring accurate service documentation. - Accounting:
Expense Approval Workflows:
Use Case: Implement Salesforce Flow to automate expense approval processes, ensuring timely approvals, accurate tracking, and integration with accounting systems.Invoice Generation and Distribution:
Use Case: Design Flows to automate the generation and distribution of invoices based on predefined triggers such as project completion or subscription renewal, reducing manual efforts and minimizing errors.Credit Control Automation:
Use Case: Use Flows to automate credit control processes, monitor customer credit limits, and trigger alerts or actions when credit thresholds are reached or exceeded.Purchase Order Approval:
Use Case: Employ Salesforce Flow to automate the approval of purchase orders, streamlining the procurement process and ensuring compliance with organizational policies.
Financial Report Generation:
Use Case: Create Flows to automate the generation of financial reports, consolidate data from various sources, and deliver comprehensive insights to finance teams in a timely manner.Check out our article Efficient Automation with Salesforce Flows
Start your learning journey?
Begin your learning journey with these three key resources:
- Trailhead module Flow build basics
- Trail: Build flows with Flow Builder.
- Explore the flow section at developer.salesforce.com. for extensive documentation, diverse learning formats (podcasts, video, blogs), and more.
- Hear about for Flow: Using Generative AI to Assist Your Flows here: https://admin.salesforce.com/blog/2023/einstein-for-flow-for-salesforce-admins
- Join Paul’s Faceboook group – see below for details
The best place to learn is by practice – dive into a sandbox environment to apply your knowledge.









